Binary Stuff
Page with a binary calculator and a binary search tutorial
Binary Math with Conversions
| Plus | Binary | Octal | Hexadecimal | Decimal | Ascii | Minus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Binary Search
Binary search is an efficient way to iterate through a SORTED list to find a requested value. This is done through checking the middle value of a list and checking if the requested value is greater than or less than the middle value. You can start to see why the requested list must be sorted. If the list is not sorted, this logic is flawed, and the binary search algorithm will no longer work.
How exactly does this work? Lets look at these amazing ms paint drawings:
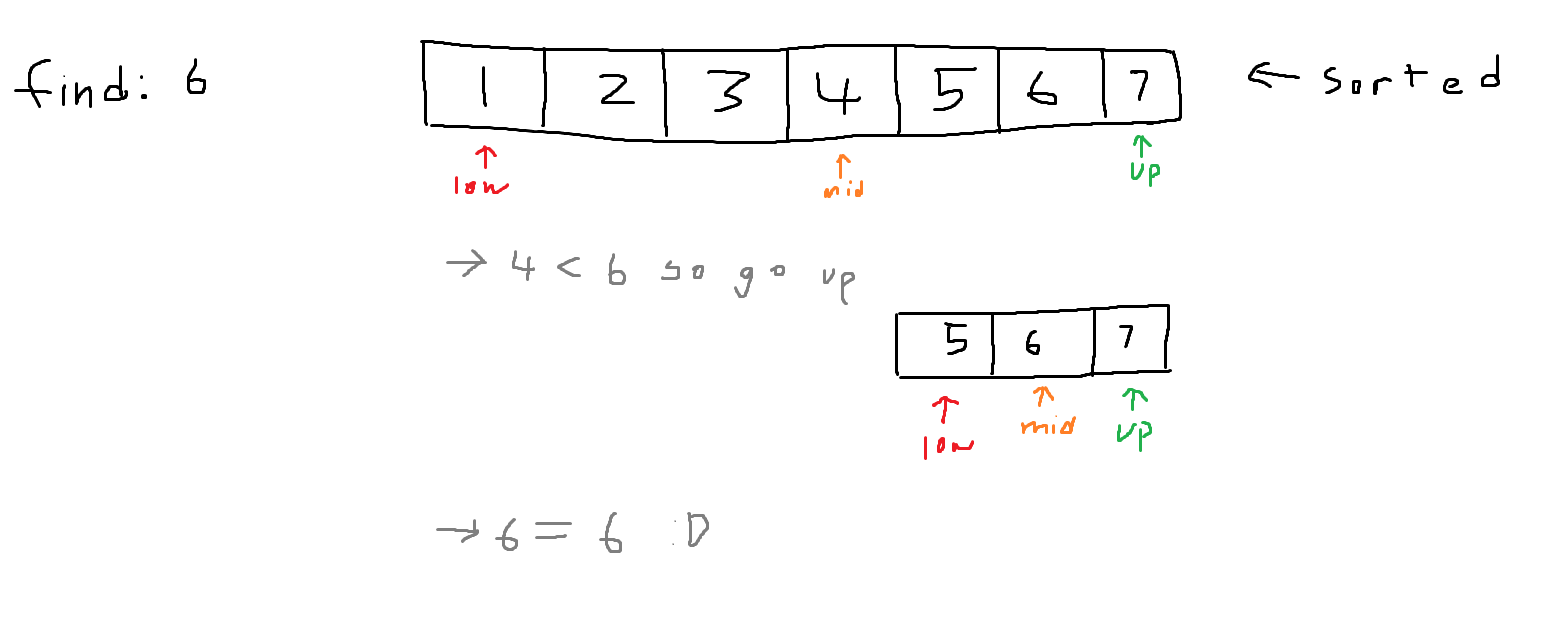
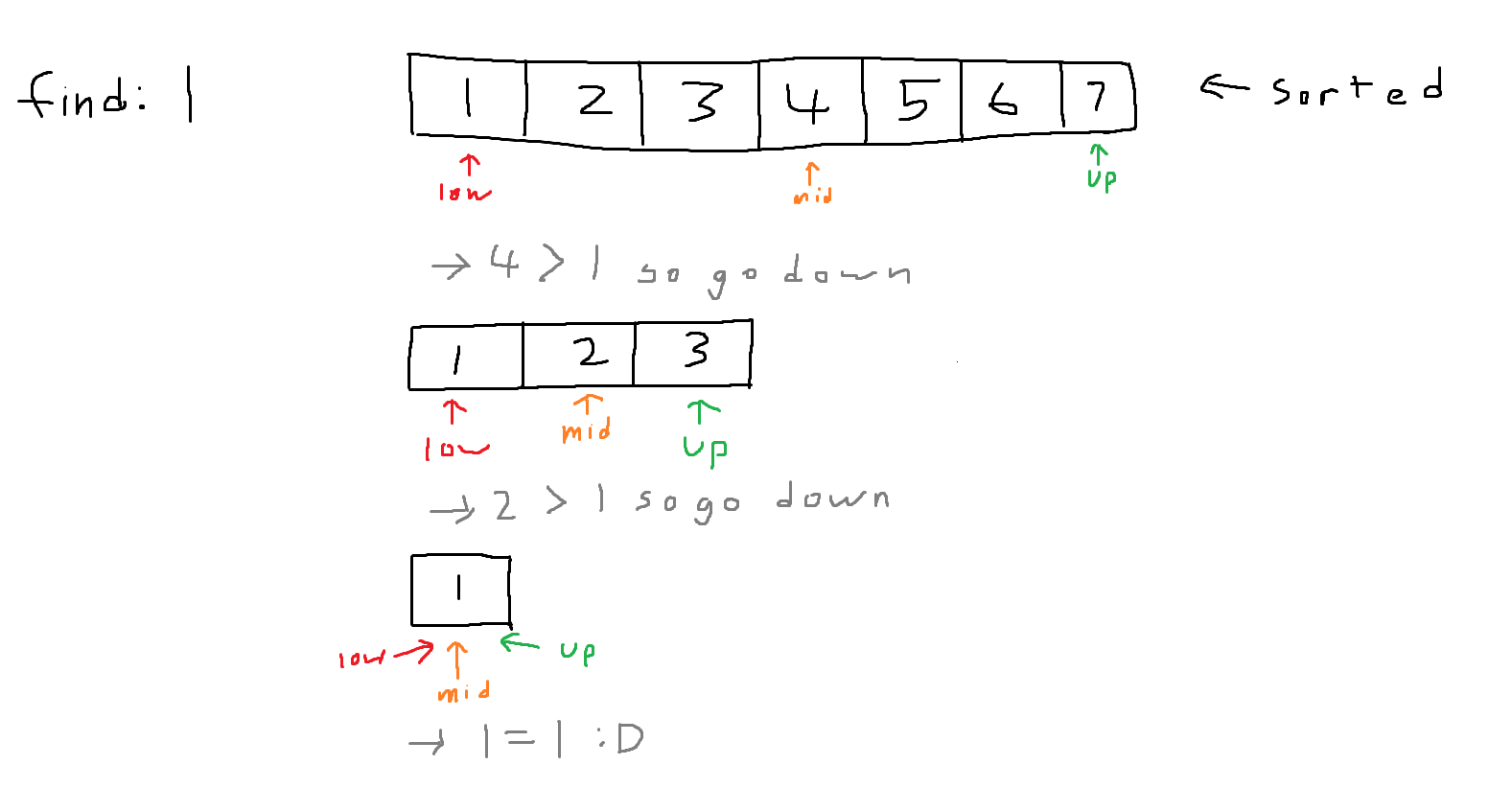
i was too lazy to make a third so ur gonna have to live with 2 :)
This algorithm is extremely efficient as the maximum number of cycles in binary search is equal to log base 2 of the closest, next power of two, to length of list.
If the array is 8 items long, the maximum possible cycles would be 3 (log base 2 of 8 is 3)
If the array is 7 items long, the maximum possible cycles would STILL be 3 as the closest power of 2 to 7 is 8.
If the array is 8 items long, the maximum possible cycles INCREASES to 4, as the closest, next power of two, is 16.
Python Example:
def binary_search(array, find): # where array is the given array and find is what we are looking for
low = 0 # the starting lower bound
high = len(array)-1 # the starting upper bound
while high >= low: # we will keep running until we run out of possible sublists...
mid = (high + low) // 2 # define the middle of the list to be the item at the index of the average of the lower and upper bound
if array[mid] == find: # if item is in the middle of the list... we found what we are looking for!
return mid # therefore, we return the index of where we found the item.
elif array[mid] > find: # if item is less than the middle of the list, this must mean that the item is on the lower half of the list
high = mid-1 # therefore, we set the upper bound of the search to be the last item of the lower half
else: # if item is neither less than or equal to the middle of the list, this must mean that the item is on the upper half of the list
low = mid+1 # therefore, we set the lower bound of the search to be the first item of the upper half
else: # if nothing is returned by the time the while loop ends, that means item MUST be missing from list
return False # therefore we tell the user that the requested item was not found
# case 1
array = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
find = 10
result = binary_search(array, find)
if result != False:
print(f"Requested value {find} is present at index {str(result)}")
else:
print(f"Requested value {find} is not present in array")
# Expected output: Requested value 10 is not present at index 3
# Question: What is the maximum number of iterations given this array?
# case 2
array = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
find = 30
result = binary_search(array, find)
if result != False:
print(f"Requested value {find} is present at index {str(result)}")
else:
print(f"Requested value {find} is not present in array")
# Expected output: Requested value 30 is not present in array
# case 3
array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100 ]
find = 83
result = binary_search(array, find)
if result != False:
print(f"Requested value {find} is present at index {str(result)}")
else:
print(f"Requested value {find} is not present in array")
# Expected output: Requested value 83 is not present at index 82
# you can see how efficient this is, only requiring 7 iterations instead of {insert number of iterations going 1 by 1 would take because im too lazy to calculate it}
# Question: What is the maximum number of iterations given this array?