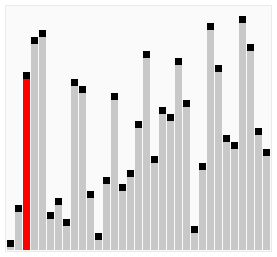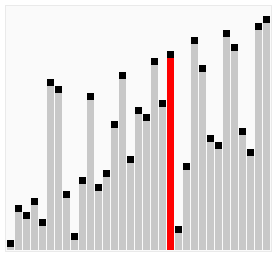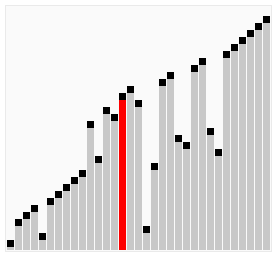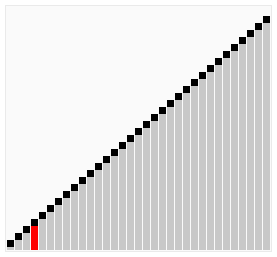
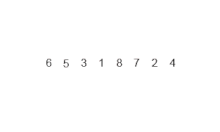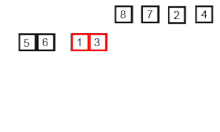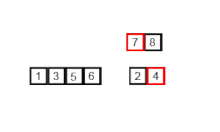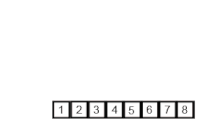Insertion Sort is probably the simplest of all sorting algorithms, and the most intuitive. We select a value and compare it to other values until it’s properly sorted. This means we need to traverse through all the values in the array twice, once to select the value and once to compare it to the other values. Thus, you traverse through the array n times, then n times again. This allows us to figure out it’s time complexity, which is O(n^2).
We start by selecting the second element of the array and compare it to the 1st. If our selected element is smaller than the 1st, we swap them. We repeat this over and over again until the list is sorted.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
INSERTION-SORT(Array)
for index = 0 to length of Array, incrementing index by 1 every time
value1 = Array[index]
// Insert value1 into the sorted array
compareIndex = index + 1
while compareIndex < length of Array and Array[indexToSort] > key
Array[indexToSort + 1] = Array[indexToSort]
indexToSort = indexToSort - 1
Array[indexToSort + 1] = key
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
private static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int i:array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public class insertionSort {
public static int[] insertionSort(int[] array) {
for (int i=1; i<array.length; i++) {
int key=array[i];
int j=i-1;
while (j>=0 && array[j] > key) {
array[j+1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j+1] = key;
}
return array;
}
}
int[] array = {5, 3, 7, 2, 8, 1, 9, 4, 0, 6};
printArray(insertionSort.insertionSort(array));
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9